Understanding the Bash shuf Command
“The shuf command is helpful for randomly shuffling input lines to standard output. The shuf command takes input from files or the standard input, randomizes the input, and gives output. It works like how you shuffle cards and pull a random output or randomly arrange the cards depending on the options that you give it.
The shuf works in three ways. You can use it as range, list, or file shuf. Let’s see the various ways you can use the shuf command.”
Using Bash shuf Command
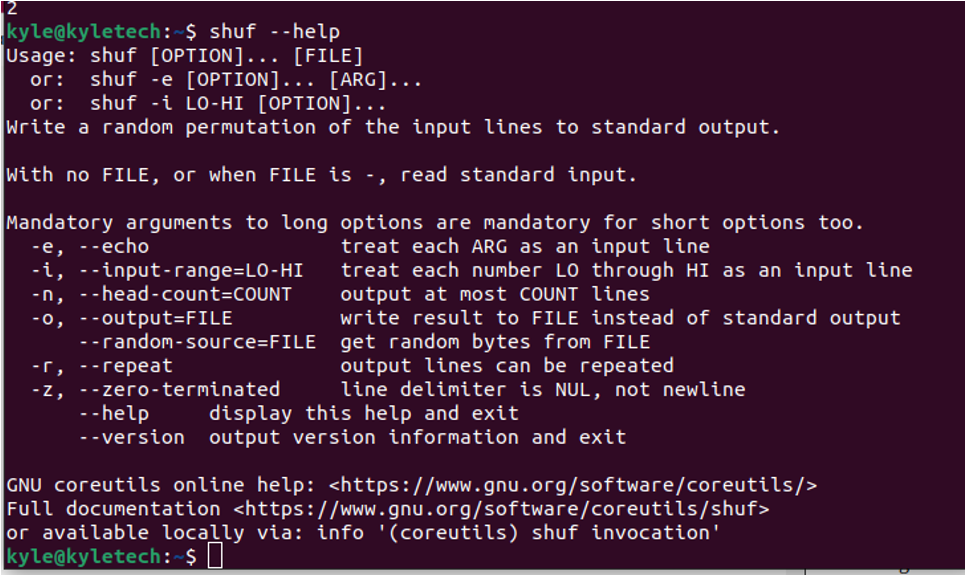
shuf is part of the GNU Coreutils, and you can open its help page to see the various options you can use.
If you execute the shuf command with no argument, it expects inputs on the command line. Once you press CTRL + D, it gives the randomized output of your input. Take a look at the image below showing how that works in action.

Also, you can combine shuf by piping the output of another command. For instance, you can shuffle the listing of files in the current directory using ls.
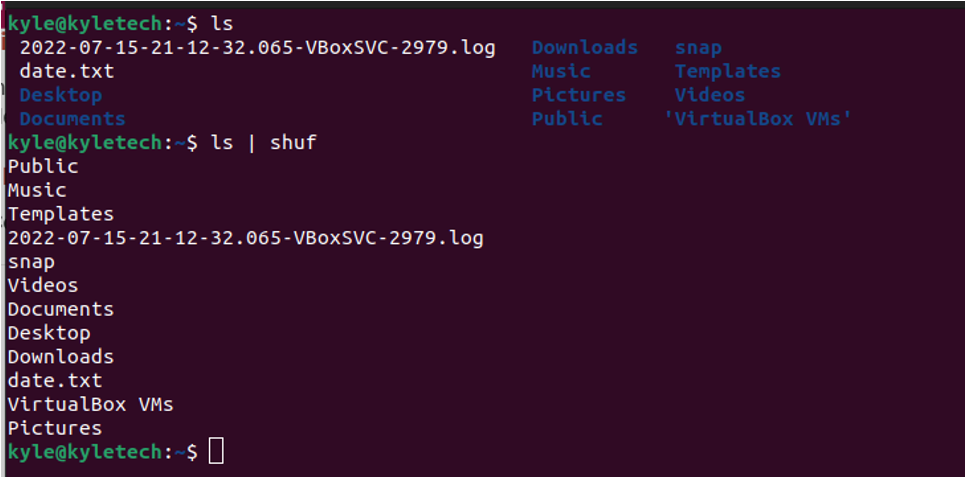
In the output above, notice how using shuf randomizes the listing of the contents of our current directory.
1. Using shuf as a File
Suppose you have a file that you want to randomize. You can use the shuf command followed by the file you want to shuffle. In this case, the file’s contents will get shuffled, and the output will be displayed on the standard output.
You can use the syntax below.
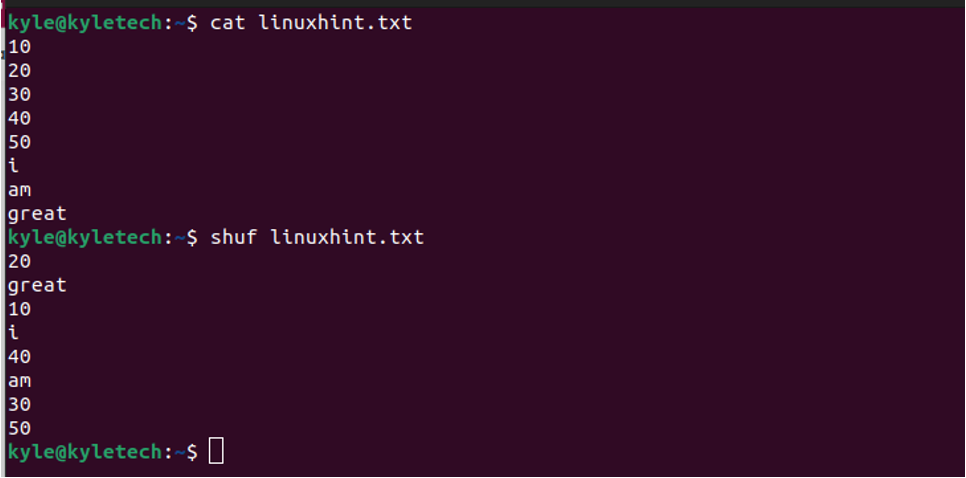
In the above example, we are shuffling all the lines in the file. However, using the -n flag, you can add the number of lines you want to shuffle. Let’s randomize three lines and see what output we get.
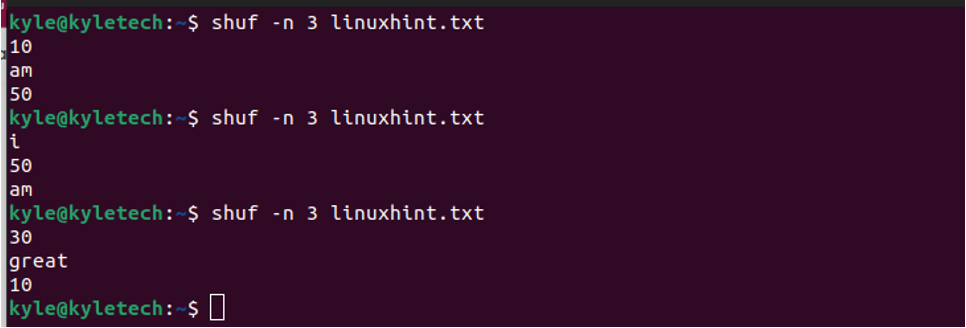
Notice how with each shuffle, we are getting random output.
2. Using shuf as a Range
You can shuffle inputs in a given range. You only need to add the lower and the upper bound. Shuf will then randomizes the input in the given range, provided you add the -i option.
Let’s have an example of randomizing numbers from 11 to 19. For that, we will run the command below.
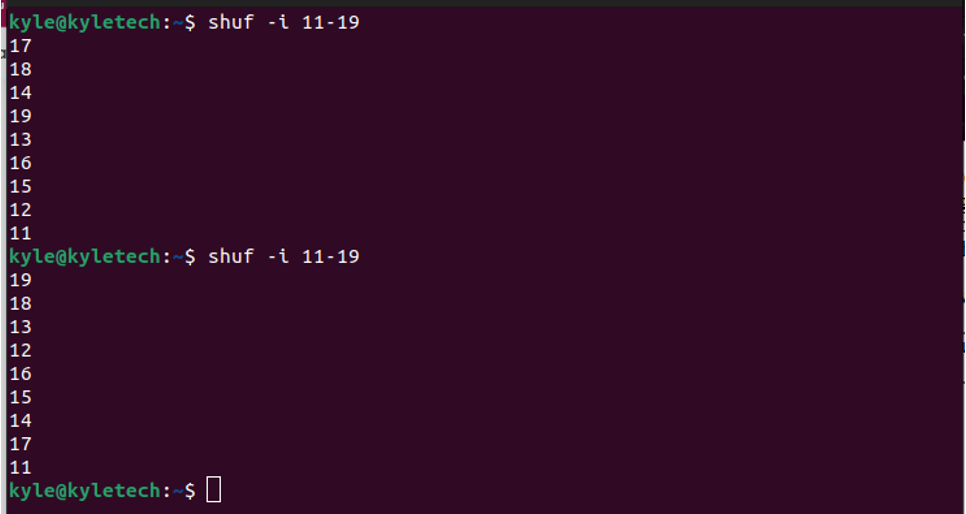
If you wanted to get only one output from the randomized range, you could use the -n as shown below.
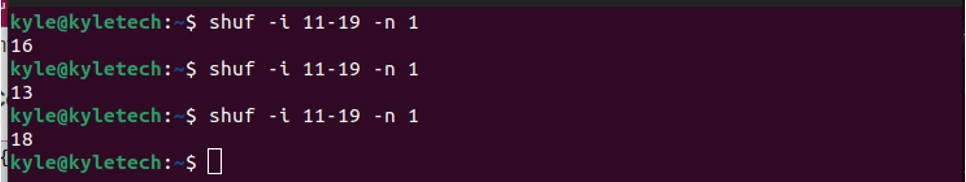
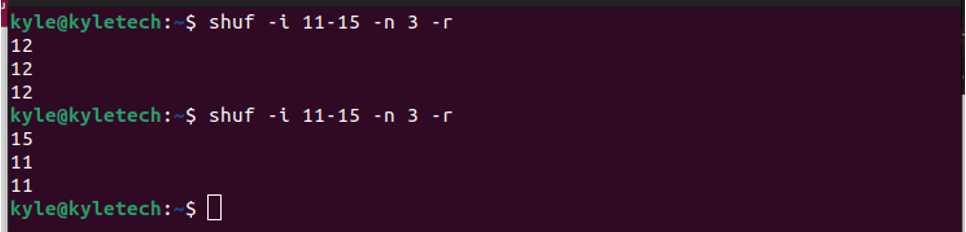
With the -n, you can only get unique output. However, add the -r flag if you want to allow the repetition of randomized output. That way, you are making it possible for the output to be the same value when displaying more than one line.
Here’s an example of shuffling a range and allowing displaying three outputs which can be repetitive.
3. Using shuf as a List
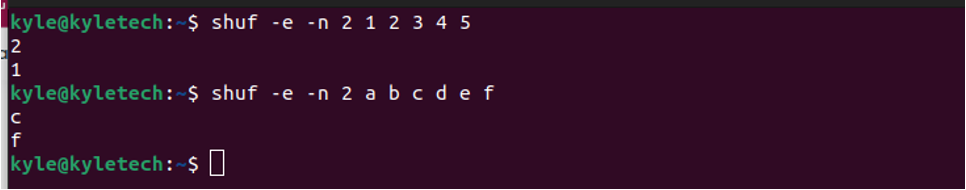
When you want to add arguments as a list in your shuf command, use the -e option. The arguments that follow the -e will be treated as the input.
Here’s an example of randomizing a list of alphabet numbers.
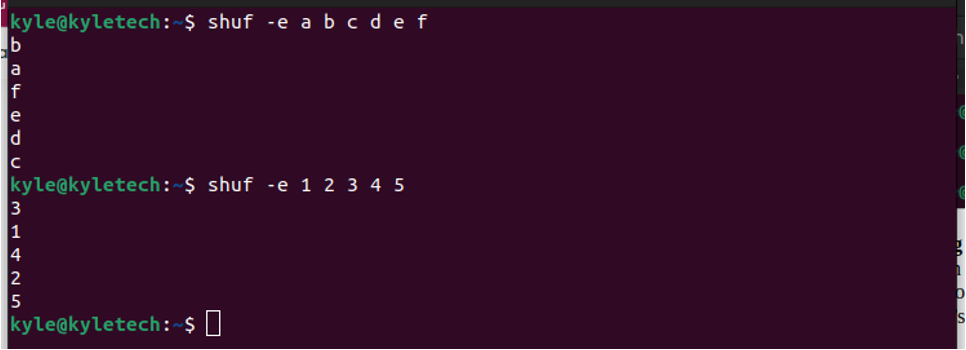
Also, you can randomize a list and decide to only output two output lines using the -n as in the output below.
Writing Output to a File
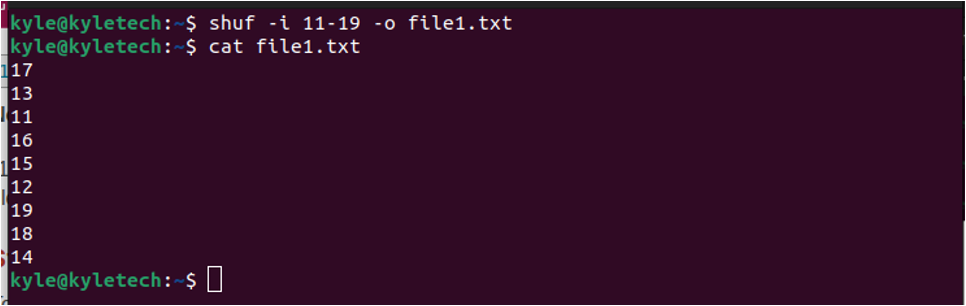
If you want to save the randomized output of your file, range, or list, you can use the -o followed by the output file name.
Let’s randomize a range and save it to a new file, as shown below.
Conclusion
Shuffling of inputs in Linux is possible thanks to the shuf command. This guide has introduced the bash shuf command and given examples of how to use it with various options to obtain different outputs. Hope you found the article helpful.
Source: linuxhint.com
