Redis PTTL
Redis uses the key-value pair approach to store its data. Hence, all the data values stored in a Redis database are referenced by a unique key.
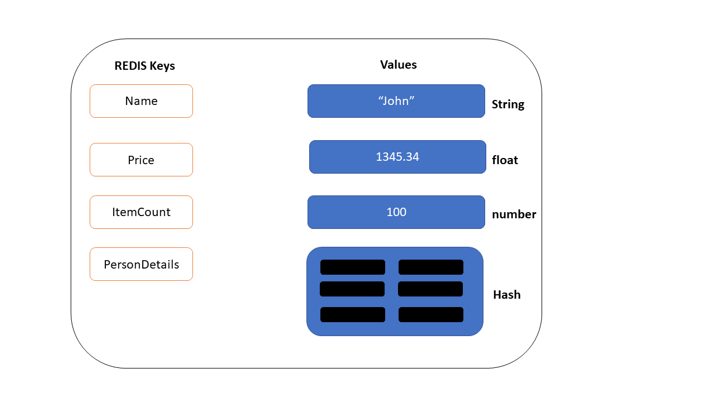
These keys tend to live forever until you delete them. Usually, we can use the ‘SET’ command to create a new key and assign a value to it. In some scenarios, you might need to set a timeout for a key.
Example – Set password reset link expiration with Redis key
Let’s assume that a user needs to reset his/her Twitter account password. The usual process is that the user clicks on the ‘forgot password’ button in the login window. This would send an email to the user with a password reset link. These links live only for a few minutes or days. Then the link will expire. We can achieve this kind of behavior by passing a Redis key in the URL. Whenever the user clicks on this link, it will redirect to the password reset page if the given key has not expired.
Create a key in Redis
Redis ‘Set’ command can be used to create a new key-value pair in the Redis data store, as shown in the following.
The ‘passwordexpirationlink:user:01’ is the Redis key and the value is ‘oldpass:123456’.
Set a timeout for the key
Since the key has been created, we can set a timeout on this key. There are two ways to set a timeout.
- Using the Redis ‘SET’ command
- Using the Redis ‘EXPIRE’ command
1. Using the Redis ‘SET’ command
The ‘SET’ command has a parameter called ‘EX’ that can be used to set the timeout in seconds. Let’s create a key with a timeout value.
The key ‘passwordexpirationlink:user:02’ will expire in 120 seconds.
2. Using the Redis ‘EXPIRE’ command
The ‘EXPIRE’ is the most popular command to set a timeout value on a key.
This is quite straightforward compared to the ‘SET’ command. The ‘passwordexpirationlink:user:02’ key will expire in 120 seconds.
Now, there should be a way to calculate or query the remaining time to live of a key. The ‘PTTL’ command allows Redis users to query this.
The ‘PTTL’ command
The ‘PTTL’ returns how much time is left before a Redis key expires. If there is no timeout value associated with a key, then this command will return -1. If the Redis key doesn’t exist, it will return -2.
Syntax
The ‘key’ is the Redis key name.
If the Redis key exists and the key is associated with an expiration time, then the ‘PTTL’ command will return the remaining time to live in milliseconds. This command is very similar to ‘TTL’, where the only difference is that ‘TTL’ returns the remaining time to live in seconds.
Let’s set the ‘passwordexpirationlink:user:02’ key’s expiration time to 120 seconds as in the previous example.
Then we can use the ‘PTTL’ command to check the remaining time to live for the key ‘passwordexpirationlink:user:02’.
Output after executing the above command several times:
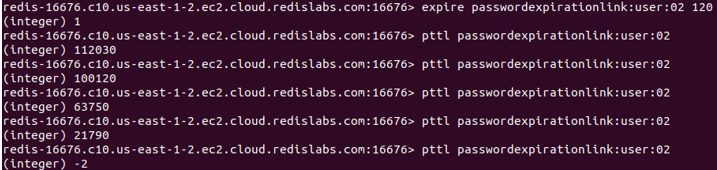
We have set the expiration time to 120 seconds, which is 120000 milliseconds. The output verifies that. The first PTTL command returns 112030, which means the ‘passwordexpirationlink:user:02’ key will expire after 112030 milliseconds or 112.03 seconds.
In the last line, the -2 has been returned. That says the ‘passwordexpirationlink:user:02’ key is already deleted or doesn’t exist anymore. It means the key has already met the expiration time and is gone forever.
The ‘PTTL’ command on a key with no expiration time
Let’s run the ‘PTTL’ command on a key that doesn’t have an expiration time associated with it. First, we are going to create a new key ‘passwordexpirationlink:user:05’.
Next, we will be running the ‘PTTL’ command on key ‘passwordexpirationlink:user:05’.
Output:
![]()
As expected, it returned -1 which means there is no timeout associated with this key.
Based on the return value of the ‘PTTL’ command, we can let the password reset link expire that we discussed in the previous example.
Conclusion
Since Redis is a key-value-based data store, keys are the direct reference for any data value. Redis ‘SET’ command is used to create key-value data in the database. This command allows us to set a timeout when creating the key-value pair. Another way of setting timeouts for keys is using the ‘EXPIRE’ command. In both ways, you can set the expiration time in seconds. The ‘PTTL’ command comes in handy when we need to query the remaining time to live for a Redis key. It returns the remaining time in milliseconds, which is different from the ‘TTL’ command.
Source: linuxhint.com
