Rebasing Remote Branches in Git
This blog will provide the process of rebasing remote branches.
How to Perform Rebasing Remote Branches Operation in Git?
To rebase the remote branch in Git, try the following steps:
- Go to the particular local repository.
- Check the remote URL list.
- Pull the latest remote repository.
- View the list of all local branches.
- Switch to the desired branch.
- Run the “git rebase <branch-name>” and push it to the GitHub hosting server.
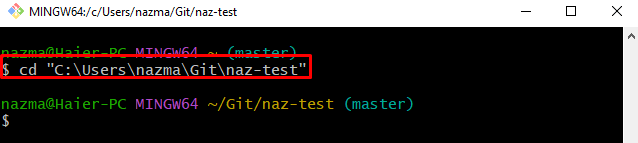
Step 1: Move to Local Repository
First, navigate to the local repository by running the “cd” command:
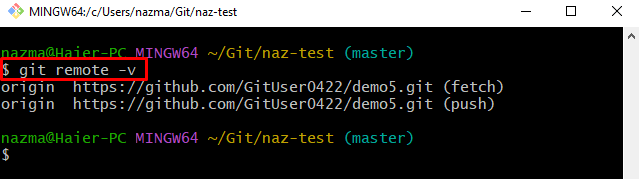
Step 2: View Remote List
Then, check the list of all available remote URLs through the following command:
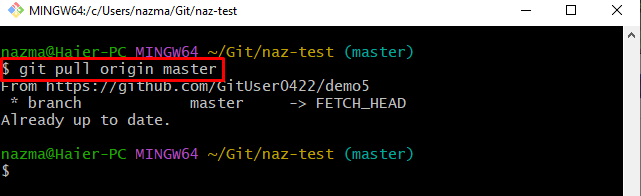
Step 3: Git Pull
Next, perform the Git pull operation to download the copy of the remote “master” branch:
According to the below-listed output, the local repository is already up to date with the remote repository:
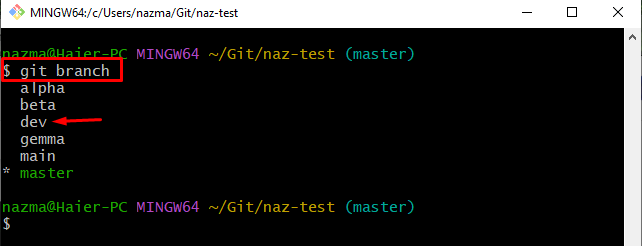
Step 4: Check Git Local Branches
After that, execute the “git branch” command to check the list of all local branches:
Here, we have selected the highlighted branch for performing the rebasing operation with the remote branch:
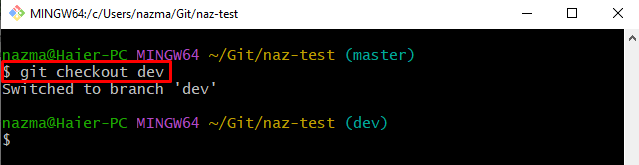
Step 5: Switch to Desired Branch
Next, switch to the targeted local branch by utilizing the “git checkout” command:
Step 6: Perform Git Rebase Operation
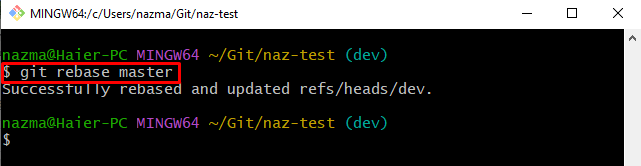
Finally, run the “git rebase” along with the desired local branch name:
As you can see, the rebasing process has been performed successfully:
Step 7: Push Rebase Branch to Remote Repo
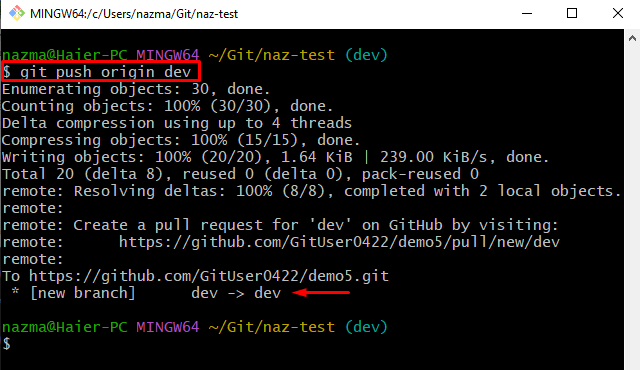
Lastly, push the rebased local branch to the remote repository by utilizing the “git push” command along with the remote URL and local branch name:
Step 8: Verify Rebase Operation
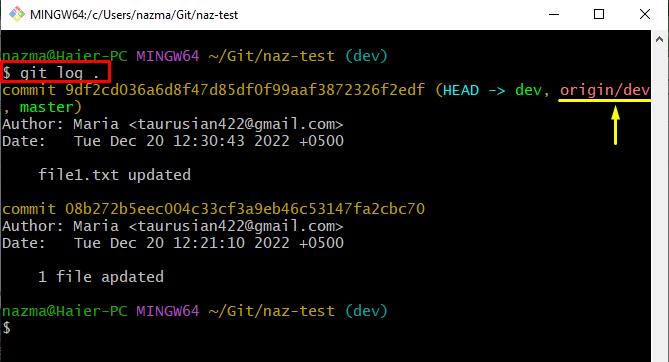
To ensure the rebasing operation, run the following command to view the Git commit log history:
In the below-given output, the highlighted remote branch indicates that the rebasing on the remote branch has been applied successfully:
We have elaborated on the rebasing of remote branches in Git.
Conclusion
To rebase the remote branch in Git, first, go to the particular local repository, check the remote URL list, and pull the latest remote repository. Then, show the list of all local branches and navigate to the particular branch. After that, execute the “git rebase <branch-name>” and push it to the GitHub hosting server. This blog illustrated the process of rebasing remote branches.
Source: linuxhint.com
