Opendir 3 C Function
The DIR data type is used to express a directory stream, although it should not be allocated by the user. We’ll look at how this method is used in some C codes in this article.
Example 01:
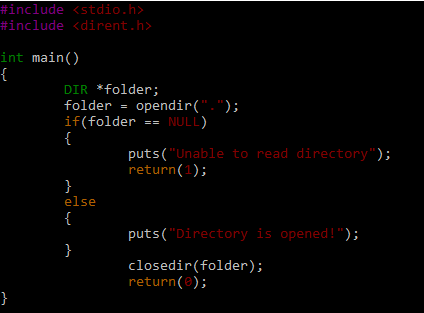
Using the VIM editor, we produced the “openDirFile.c” file. You can choose any editor, including nano. When the file is opened in the VIM editor, type the code shown in the following screenshot. The current directory which is abbreviated as the dot(.) is opened and closed in the following code:
The output of the previous code is:
![]()
The functions for reading and manipulating directories/folders are available in the C language. It allows your programs to handle the files and perform other file-related operations.
Example 02:
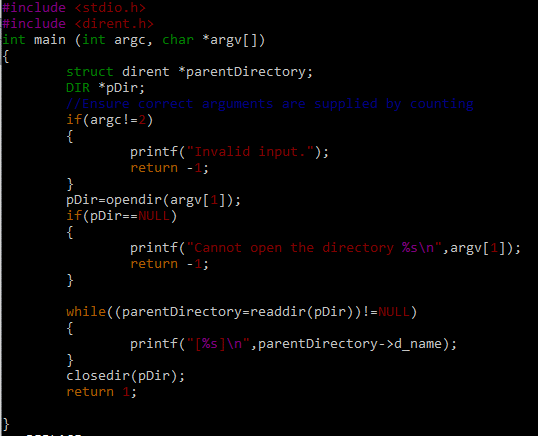
Now, we write the advanced code to understand the complete concept and learn how to execute and compile it. The header files are included in the first two lines. Following that, the main function signature is called. You can see that we received the directory name from the main function’s command line inputs and passed it to the opendir function. Within the main block function, the first line is a direct structure, which is essentially a representation of the directory system. It may contain the file’s serial number as well as the names of the folders found in the supplied path.
We defined a pointer-type variable called pDir in the second line of the code. Following that, there is a conditional statement that is mostly used to check whether the command line contains the correct amount of arguments. If the values supplied are invalid, print the message and exit the function without performing the following code. If the input is correct, store it in the pDir variable and verify that it is not NULL. If it is NULL, it signifies that there is no directory or the path is incorrect or illegal.
In that case, the return statement is executed and the compiler terminates the execution of the lines of the code below it. If the pDir parameter is not NULL, it indicates that the directory name provided by the user is legitimate and correct and that the directory exists, which may include the files and folders. The readdir function is used inside the while loop in the following lines of code to display the names of files and folders that exist in this directory. At the end of the line, we close the pDir variable. To get a comprehensive list of the files that you generated in the working directory, use the “ls” command. See the following screen for more details:
After that, use the GCC compiler to compile the C file. If your system doesn’t have a GCC compiler, use the following command to install the compiler on your operating system or virtual machine:
$ sudo apt install build-essential
You may check if you have already installed it on your operating system or virtual machine by executing the following command:
Now, you have everything you need to compile and run/execute the C code. To begin, use the command given in the image to build the code. After that, type “gcc” and the name of the file that you want to compile or produce an object or output file for. If you do not specify the remaining arguments in the command line, the output will be generated and saved in an “a.out” file.
However, if you want to name your output file whatever you like, type “–o”. Then, type the name of the output file followed by the “.out” extension.
![]()
Before moving further, a few more things that you have to know is that in Macintosh and later Windows, the term “folder” is used. It used to be a directory, a list of files saved on the storage media. To execute the file, just use the following command which includes the “./OUTPUT FILE NAME.out”. As you can see, if we execute the output file without any command line arguments such as a directory path, we get an error stating that the input is invalid.
![]()
When we execute the output file, we provide the directory name in the following screen. You may see the list of files and folders that exist in the works directory after pressing the enter key.
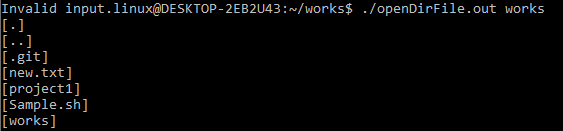
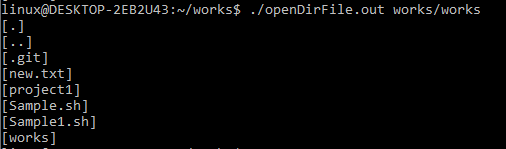
Another option for supplying the directory name is to type the entire directory path or only the part of the path where we are now located. In the following example, we supply the “works/works” which include our current work followed by works, and then inside the works folder.
As you can see in the following example, we specified a directory or folder name that does not exist in the current directory where our output file is located. If pDIR returns NULL, we display or report an error indicating that the directory cannot be opened.
![]()
Conclusion
This article is all about the use of the opendir() function of C in Kali Linux with the demonstration of its working process. We discussed the simple yet efficient examples of C to achieve the required results. The other POSIX functions are used for the side help in the codes.
Source: linuxhint.com
