Java Getters and Setters
When we do the program, we tend to work with many user-defined and built-in methods. Java programming is also diverse when it comes to the use of functions. The special class methods known as getters and setters are employed in Java programming to read from and apply to an entity’s attributes. In Java, the setter function serves to set up or populate corresponding class fields while the getter function serves to read the value stored in the variable or retrieve the content. This procedure can be performed with inheritance as well. Most classes come with getter and setter methods by convention. Nevertheless, by specifically declaring the getter and setter functions, we may override the standards. In this regard, we are going to explain the usage of getter and setter functions in Java programming.
Example 01:
In our example of Java, we are going to discuss the use of getter and setter functions to set the values for data members and fetch them accordingly. Make sure that your Windows system have a Java programming tool like Eclipse IDE already configured. So, we need to create a Java code file in Eclipse IDE with the name “main.java” as shown in the below image. The java file has started its script with the declaration of a package “test”, Java project name. This Java program contains two classes in it. main() class contains the main driver function and the other class “test” contains getter and setter functions.
The “test” class has been started with the declaration of a string variable named “color” containing a private access modifier which can be accessed in its class only. Although we cannot access this private data member in the main class, we can use it through getter and setter functions. So, we have defined a string “get” function and a void “Set” function. The get function helps you fetch the value of the string “color” and the set function helps you set the value of this variable passed by the main() method.
The main() method of the main class contains the creation of a “test” class object “t”. The object has been used to call the set() function of the “test” class by passing it a string value in parameters. The statement “System.out.println” will be displaying that value by calling the get() function. The same thing has been repeated.

After this Java program execution, we got the value of a string variable displayed at the output console after calling the “set” function two times using the child class object. This was easy to fetch the private type string value of one class to another using getters and setters because we were using both classes within the same Java code file.

Example 02:
In the first example, we have seen the method of using the getter and setter functions to set and fetch the values of a private data member for one class from the other class using the object in the same file. It was smooth to implement such sort of example because it does get executed successfully and does not return any error.
Now, we will try to get a private data member of one class from the other class that has been defined in another Java file using the getter and setter functions. Firstly, we will be creating a main() class in the main.java file. This file contains a public class “main” with the private string type data member “Subject” and its getter, setter functions.
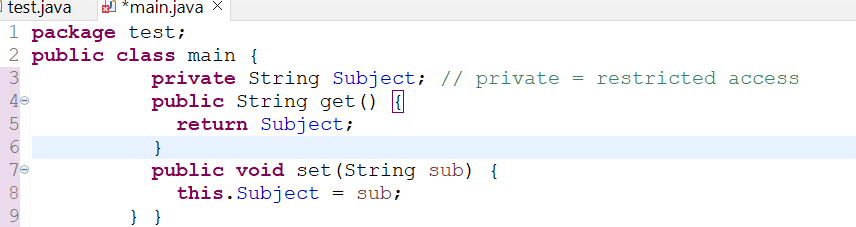
Within the other file “test.java”, we have created a test class that contains the main() driver function. The object “t” for the other class created in the “main.java” file has been created. The object “t” got employed to assign value to the “main” class string variable “Subject”. Without using the getter and setter, we are using the object “t” to display the value of a string variable.
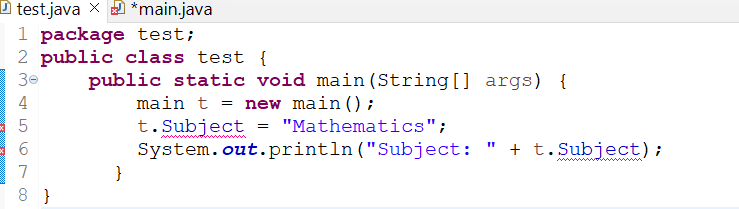
As we are not calling the get and set function in the test.java file and also declaring the string variable with the private access modifier in the main.java file, it would be showing us an error on the string name “Subject” as shown in the image below.
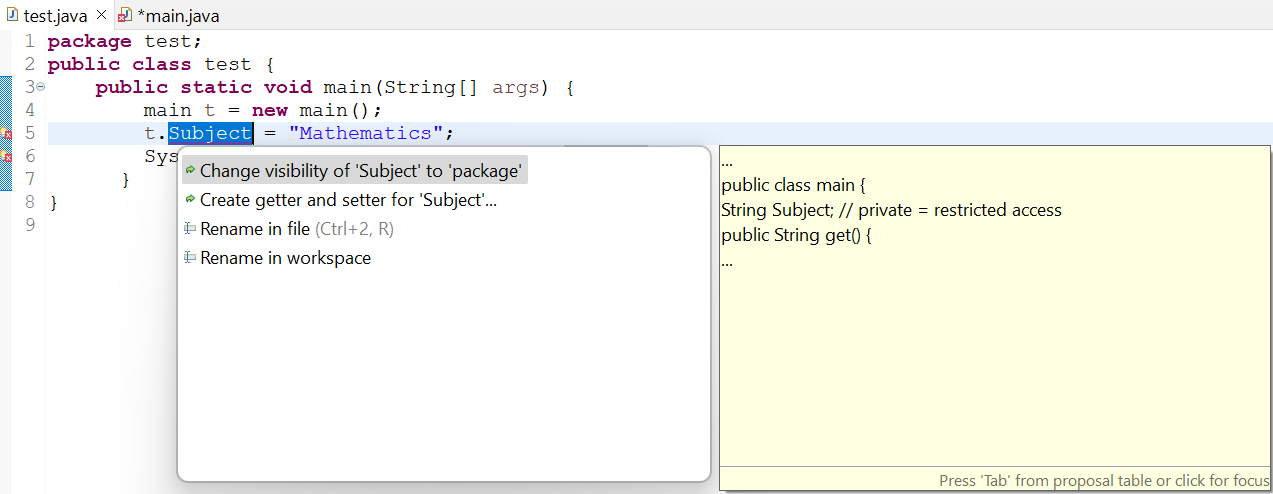
When you run this code in the Eclipse IDE java tool, it will throw an exception that the variable “Subject” from the main() class is invisible or inaccessible within the test.java file due to the use of a private access modifier.
To avoid this error in Java programming, you need to first change the type of access modifier used with the string variable “Subject” of a main.java file. Yan can use the “public” or “protected” access modifier when you have been working with two different Java files to perform inheritance through getters and setters. Thus, we are now using the protected access modifier for the string variable “Subject” of the main() class used in the main.java class. Do not change the rest of the Java code.
Now, it is time to use the same “test.java” class to call the “Subject” string variable from the other main.java file for displaying at the console output of Eclipse IDE. You do not need to call the get and set functions in this file as we have already created the class main object “t”. Lastly, you must display the value of the string “subject” that has already been passed to get/set.

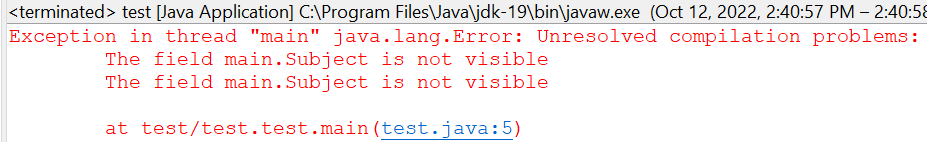
After this code execution, we got the subject “Mathematics” presented as the Eclipse IDE tool. You can see that there is no need to call the getter and setter functions in the main() method.

Conclusion
This guide is to understand the getter and setter functions of java. The introduction explains the purpose of the getter and setter functions shows you a simple method to utilize them. The other example explains how the getter and setter functions are helpful in two different java files.
Source: linuxhint.com
