Arrays.stream() Method in Java
This write-up will discuss the utilization and implementation of the “Arrays.stream()” method in Java.
What is the “Arrays.stream()” Method in Java?
The “stream(T[] array)” method of the “Arrays” class in Java returns a sequential stream of the array passed as its argument. This array can comprise multiple data types, i.e., “Integer”, “String”, etc.
Syntax
In this syntax:
- “static” refers to the method type.
- “T[ ] array” corresponds to the array of any data type.
In the above syntax:
- “static” signifies the method type.
- “T[ ] array” points to the array of any data type.
- “int init” is the start index(inclusive).
- “int last” indicates the last index(exclusive).
Before heading to the examples, make sure to include the following packages to access all the classes, methods, and working with the streams, respectively:
import java.util.stream.*;
Example 1: Applying the “Arrays.stream()” Method in Java to Return a Sequential Stream of the “String” Array
In this example, the “Arrays.stream()” method can be applied to display a sequential stream of the string values accumulated in the particular array:
According to the above code, perform the following steps:
- Firstly, define a “String” array having the provided values.
- In the next step, apply the “Arrays.stream()” method having the defined array as its parameter. Also, specify the array type, i.e., “String” and the return type “Stream”.
- Lastly, apply the “forEach()” method to iterate along the stream and display the string values in an array in a sequential way.
Output
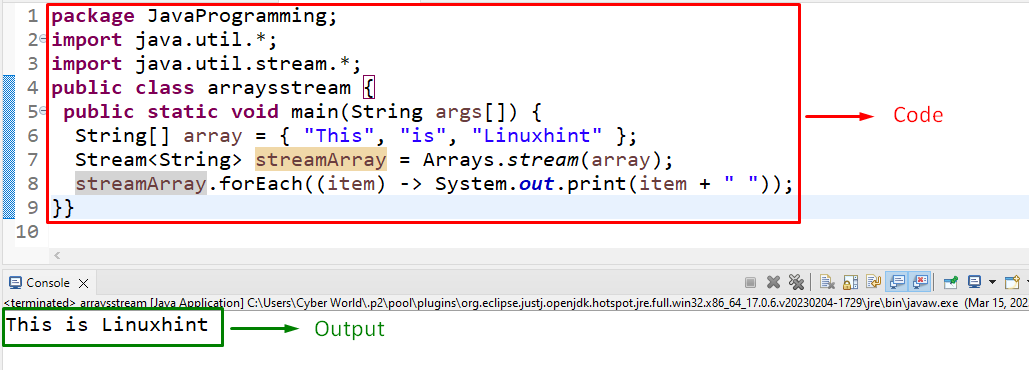
In this output, it can be observed that the separated string values in an array are displayed in a sequential stream.
Example 2: Applying the “Arrays.stream()” Method in Java to Return a Sequential Stream of the “Integer” Array
This example can be utilized to apply the discussed method to log a sequential stream of the “Integer” array:
According to the above lines of code, repeat the discussed approaches for defining an array, i.e., “Integer”(in this case). After that, likewise, apply the “Arrays.stream()” method to return a sequential stream and display the integers in an array sequentially.
Output
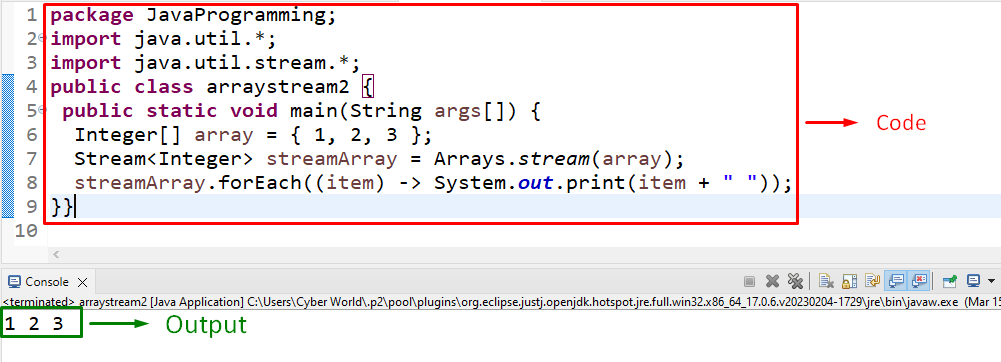
In this outcome, it can be analyzed that the integers are displayed in a streamlined manner.
Example 3: Applying the “Arrays.stream()” Method in Java to Return a Sequential Stream of the “Specified” Values in a String Array
In this particular example, the discussed method can be implemented to return a sequential stream of the specified string values by referring to their indexes:
In this code snippet:
- Likewise, declare a “String” array having the provided string values.
- In the next step, apply the “Arrays.stream()” method containing the specified array and the indexes of the values, respectively, as its parameters.
- Note: The value against the specified end index will not be included in the resultant stream.
- Finally, display the accumulated string values in a stream via the “forEach()” method.
Output
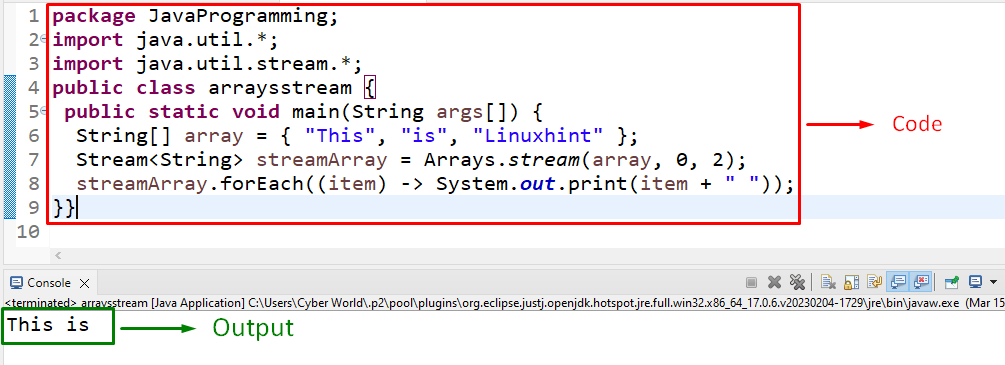
The above output indicates that since the string value “Linuxhint” is at index “2” so it is not returned in the stream.
Note: If there is a requirement to utilize both the data types, i.e., “Integer” and “String” for returning a stream, utilize the “Object” type instead.
Conclusion
The “stream(T[] array)” method of the “Arrays” class in Java returns a sequential stream of the array passed as its argument. This method can be applied to simply return a sequential stream of multiple data types and the stream of the specified values via indexing as well. This article demonstrated the implementation of the “Arrays.stream()” method in Java.
Source: linuxhint.com