Application Sandboxing with Firejail in Linux
If you have an untrusted application that needs to be run in your Linux system, you can use a sandbox to run the application in a limited environment. In this way you can use the untrusted application without worrying about the security of your system.
Sandboxing with Firejail uses namespaces, SECCOMP, and kernel capabilities to run untrusted applications in their own individual sandboxes. This can help prevent data leakage between applications, and it can help prevent malicious programs from damaging your system.
Installing Firejail
To install Firejail on your Debian/Ubuntu/Raspbian machine, use the following command:
#apt update #apt install firejail
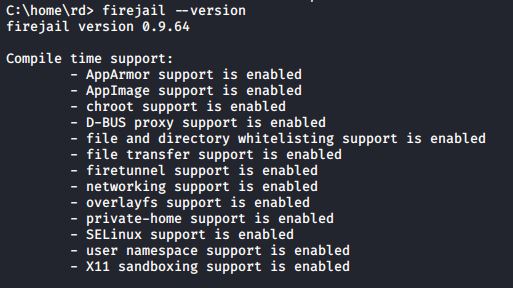
After installing, you can run the following command to check the installed version
#firejail –version
Firejail Profiles
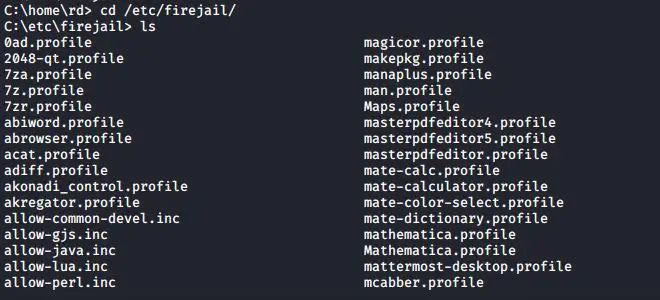
When you invoke an application with Firejail, it will automatically load the correct profile for that application, if one exists. If you invoke an application that doesn’t have a profile, Firejail will just load a generic one. To see the profiles, cd into /etc/firejail and take a look:
Running an application using firejail
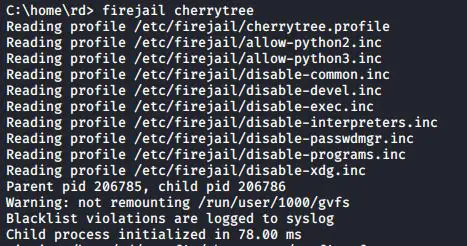
The simplest way to use Firejail is to preface the name of the application you want to run with firejail. Let’s start with cherrytree:
#firejail cherrytree
In the following figure we can see how terminal window looks like when we run application with limited environment
Tracking Sandboxes
You can also check whether your application is running in a sandbox or not by listing all the sandboxed applications. Execute the following command to view all the applications that is running in a limited environment
#firejail --list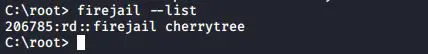
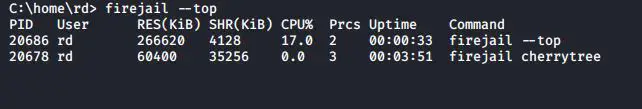
You can also run the top command along with firejail to display all the processes running under the firejail. Run the following command in the terminal window to display all the processes
#firejail --top
Shutting Down Sandbox
In case a sandbox is not responding, you can shut it down from the terminal window by just typing a command. First of all run the firejail command with –list option to list all the sandboxes. After listing all the sandbox, note the PID of the sandbox to be shutdown and run the following command
#firejail --shutdown=PID
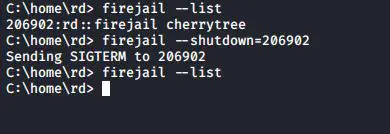
When you run the above command, it will shutdown the sandbox specified by PID
The post Application Sandboxing with Firejail in Linux appeared first on The Linux Juggernaut.
Source: The Linux Juggernaut